Response of the Earth System to Global Change
The JModels elucidate the natural cycling of nutrients and carbon in the oceans and the natural operation of the Earth’s radiation balance. They can also be used to examine some aspects of the operation of the perturbed Earth. Human activities are making large impacts on the ocean, and on the Earth’s radiation balance, and the carbon and radiation budget models in particular given an indication of the likely effects of some of these changes. Some of the changes that can be examined are:
1) Ocean acidification: due to invasion of fossil fuel CO2 into the ocean.
2) Future ocean C sink: will any of the multiple ways in which the ocean is being changed make a large difference to how much CO2 it absorbs?
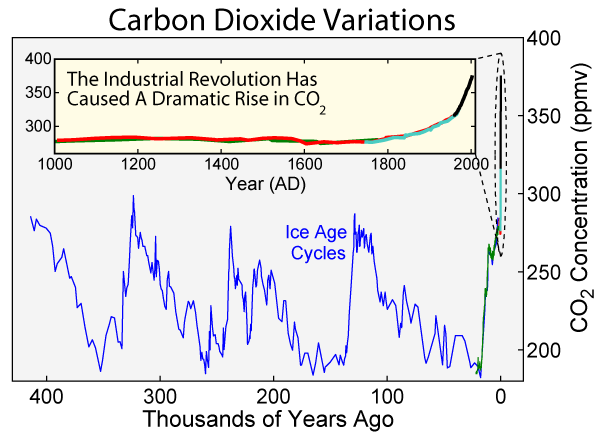
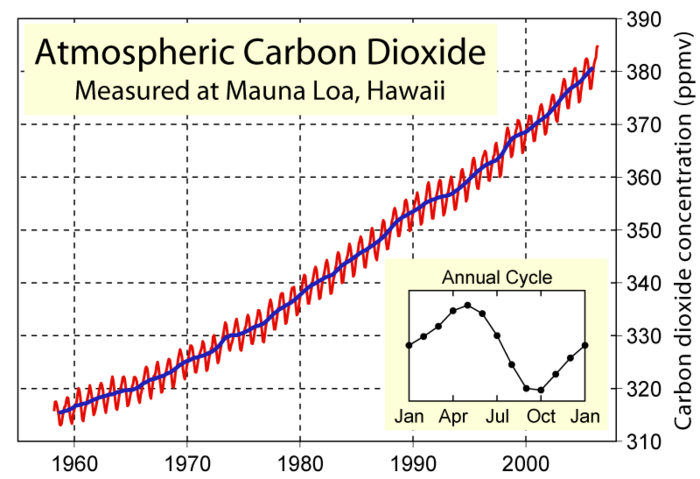
3) Long-term CO2: what legacy will our burning of fossil fuels leave behind for future generations, including our descendants living many thousands of years in the future?