Carbonate Compensation
The ocean has an inbuilt negative feedback process for stabilising the saturation rate with respect to calcium carbonate (Ω), albeit one that takes many millennia to counteract perturbations. This process is called carbonate compensation (Zeebe and Westbroeck, 2003). It involves automatic adjustment of the CaCO3 lysocline in response to any deviations in the CaCO3 saturation state of seawater. The lysocline is the depth at which significant amounts of calcium carbonate start to dissolve on the seabed. Above the lysocline, nearly all of the CaCO3 that falls to the seafloor accumulates in the sediments. Below the calcite lysocline the waters are corrosive to it, leading to dissolving of some or all of the CaCO3 within the sediments. The CaCO3 saturation state is equal to ([CO32-] [Ca2+] / Ksp), where [CO32-] is the concentration of carbonate ions in seawater, [Ca2+] is the concentration of calcium ions and Ksp is the solubility product. In practice, over timescales less than a million years or so, values of both [Ca2+] and Ksp) are bound to remain more or less constant in the ocean. Variations in the value of Ω are therefore determined by variations in the value of [CO32-], and stabilising Ω is equivalent to stabilising [CO32-].
Response to [CO32-] Perturbed Downwards
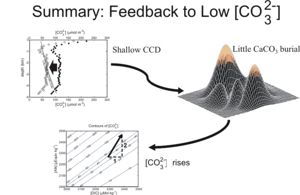
As illustrated in the diagram to the right, carbonate compensation involves the adjustment of the depth of the CaCO3 lysocline in the ocean in response to changes in Ω. It acts as follows. As the ocean becomes more acid (as is happening at present), carbonate ion concentration ([CO32-]) drops. Because the vertical profile of [CO32-]c(z) (the saturating value of [CO32-], i.e. value at which Ω=1 where seawater is neither under- nor super-saturated relative to CaCO3) does not change, the intersection point of the saturating and the actual [CO32-] moves to shallower depths. This causes a shallowing of the saturation horizon (depth at which Ω=1). Although the lysocline does not lie exactly at the saturation horizon, the two are interlinked. The lysocline typically lies somewhat deeper in the water than the saturation horizon, but the two depths change together in response to changing [CO32-].
The depths of the saturation horizon and lysocline are very sensitive to deep water [CO32-]. For instance, even only a 25% drop in average deep water [CO32-], taking it down from about 90 μMol kg-1 today to 67.5 μMol kg-1 in the future would cause the global saturation horizon to shallow by about 2 km. Much larger decreases in deep [CO32-] are in fact forecast for the future, depending on future Co2 emissions. A model of ocean acidification predicts, under almost all emissions scenarios, that average lysocline depth will be shallower than 0.5 km by the year 2300, compared to depths of at least several kilometres in most locations at present.
Shallowing of the lysocline will increase global dissolution and decrease global burial. This will tend to oppose the low [CO32-] values, by driving an imbalance between the riverine input of dissolved calcium and carbon and their removal in buried calcium carbonate. Rivers continue pouring in 'dissolved carbonate', but the ocean stops (slows down) its burial of CaCO3. The chemical equation for calcification is given by:
Ca2+ + 2HCO3- → CaCO3 + CO2(aq) + H2O
and dissolution is the reverse reaction.
Dissolution of 1 Mole of CaCO3 (or an equivalent reduction in CaCO3 burial) therefore leads to addition of 1 Mole of dissolved inorganic carbon to seawater, together with a simultaneous addition of 2 Moles (charge equivalents) of alkalinity. When the carbonate chemistry is calculated out, these changes to DIC and alkalinity induce an increase in the carbonate ion concentration, completing the negative feedback.
Response to [CO32-] Perturbed Upwards
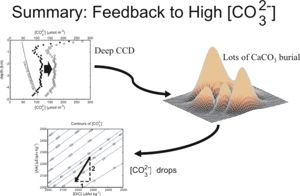
Chain of events set in motion by an abnormally high saturation state in seawater, leading to a return towards lower values
As illustrated in the diagram to the right, the carbonate compensation response to elevated saturation state is as follows. A rapid elevation of the carbonate ion concentration ([CO32-]) to higher-than-normal values will be accompanied by a transition to the ocean being more than normally supersaturated. Because the vertical profile of [CO32-]c(z) (the saturating value of [CO32-], i.e. value at which Ω=1 where seawater is neither under- nor super-saturated relative to CaCO3) does not change, the intersection point of the saturating and the actual [CO32-] moves to deeper depths. This causes a deepening of the saturation horizon (depth at which Ω=1) and lysocline.
Deepening of the lysocline will decrease global dissolution and increase global burial. This will tend to oppose the high [CO32-] values, by driving an imbalance between the riverine input of dissolved calcium and carbon and their removal in buried calcium carbonate. Rivers continue pouring in 'dissolved carbonate' at the same rate, but are now outweighed by the increased burial of CaCO3.
CaCO3 burial leads to removal of 1 Mole of dissolved inorganic carbon from seawater, together with a simultaneous removal of 2 Moles (charge equivalents) of alkalinity. When the carbonate chemistry is calculated out, these changes to DIC and alkalinity induce an decrease in the carbonate ion concentration, completing the negative feedback.
Speed of Carbonate Compensation
The carbonate compensation-induced changes to ocean carbonate ion concentration will continue until the original, steady-state, carbonate ion concentration is re-attained. The e-folding response time (the time for the deviation of a variable from its equilibrium value to decrease by a factor of e) for carbonate compensation has been estimated in different modelling studies at between 6000 and 14000 years. It will therefore not work quickly enough to prevent ocean acidification (operating over a timescale of centuries) from making dramatic changes to [CO32-] and Ω. Over longer timescales, however, it buffers their values. It is an important facet of the Earth System response to various upheavals.
Other Processes Stabilising Ω
Carbonate compensation as described here is brought about purely by changes in lysocline depths in response to changes in Ω. There are several other aspects of oceanic CaCO3 cycling that most likely also contribute to maintenance of Ω near to its equilibrium value. :
1. production of CaCO3 may well decline in a more acidic surface ocean, leading to a lighter rain of particles out of the surface ocean and hence to a lighter rain to the sea floor;
2. CaCO3 that fell to the seafloor in pre-industrial times, before any ocean acidification, may also be affected. As this CaCO3, lying at or near to the surface of the sediments, comes into contact with increasingly acidic deep bottom waters, it is likely that some of it, finding itself now lying beneath a suddenly shallower lysocline, will be chemically eroded via dissolution.
3. the combination of warming, higher CO2 and increased rainfall in a warmer world may also hasten the rate of weathering of limestone, dolomite and chalk rocks on land, leading to an increased supply rate of calcium and carbon to the oceans.
These are not incorporated into the carbon model (although the first can be optionally added using the Model Parameters window).
Other related pages
Carbon model
Earth System response to various upheavals
Ocean acidification
References
Zeebe RE & Westbroek P (2003) A simple model for the CaCO3 saturation state of the ocean: The "Strangelove", the "Neritan", and the "Cretan" Ocean. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 4: article number 1104.
Broecker WS & Peng T-H (1987) The role of CaCO3 compensation in the glacial to interglacial atmospheric CO2 change, Global Biogeochem. Cycles, 1: 15–29.
External links
Description of the chemical element carbon
Description of the carbon cycle,
carbonate compensation depth in the oceans
Saturation (first meaning)